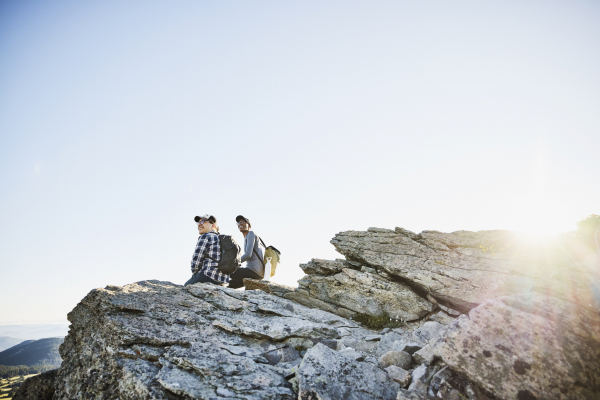
Summer is an ideal time to take a hike, especially if you have the opportunity to explore one of our country’s many state and national parks. But if you venture far from home, it’s essential to make sure you’re prepared for the local climate and other conditions you may encounter on the trail, especially if you’re not an experienced hiker. Higher temperatures than you’re accustomed to or other extreme weather can be deadly.
“If you’re taking a hike in mid-July in the Arizona desert, there’s a very different list of considerations than if you’re in the mountains of Montana or the forests of North Carolina,” says Dr. N. Stuart Harris, chief of the Division of Wilderness Medicine at Harvard-affiliated Massachusetts General Hospital. Here’s a run-down of what to consider before you hit the trail.
Traveling companions, safety notifications, and orientation
First, it’s safer to travel in pairs or a group of people. But always tell someone not on your hike where you’re going, your anticipated route, and when you expect to return. National parks often require reservations or permits for overnight stays or treks to certain locales, and keep a record of day-hikers, so sign up as requested. If you end up getting injured or lost, the information can make a huge difference in locating you more quickly.
Remember to bring a map and know how to orient yourself. In many wilderness areas, cell service may be spotty or nonexistent, so don’t count on using your phone’s GPS.
In the desert, you may be able to see for 50 miles in the distance. But if you’re in a steep, wooded area, you might not be able to see 100 yards ahead and it’s much easier to become disoriented, says Dr. Harris.
Be ready for heat, humidity, and other weather hazards
Check forecasts first. Always check the forecast so you can be prepared for weather changes. Temperatures may drop and wind may increase as you climb higher. If you’re in an area prone to thunderstorms, lightning injury should definitely be on your radar, says Dr. Harris. Learn these lightning safety tips from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Because these storms usually strike in the afternoon, you can minimize your risk by hiking in the earlier part of the day.
Hydrate well. During any type of exercise — especially hiking, which often demands a fair bit of exertion — be sure to drink extra water to replace the fluid you lose from sweating. On a warm day, you might not notice you’re sweating if it’s breezy. Pay attention to any signs or alerts advising hikers on how much water is best to carry.
Consider humidity. Temperature isn’t the only consideration, however. “If you’re in Arizona and the temperature is over 100° F, your body may be better able to release heat by sweating than if you’re in a very humid area,” says Dr. Harris. In the Great Smoky Mountains, for example, the temperature in July may be only in the high 80s. But humidity levels usually hover around 75% or higher. That means your sweat will evaporate more slowly, so your body’s natural cooling mechanism doesn’t work as efficiently. Be sure to rest and hydrate if you start feeling overheated.
What to wear and bring
Many park websites offer detailed safety tips specific to the terrain and weather you may encounter on a hike, so check before you go. Five basics to consider are as follows:
- If your hike involves rocky or uneven terrain, hiking boots will offer more support than tennis shoes.
- You’ll be more comfortable in lightweight, moisture-wicking clothing, but bring extra layers and rain gear, if the weather forecast suggests this is appropriate. Temperature drops can be surprising in some places when the sun wanes, so be prepared to layer up as needed if you’re out longer than expected.
- Wear a wide-brimmed hat and sunglasses to shield you from the sun’s glare — and don’t forget to apply sunscreen to all exposed skin before you set off.
- Along with plenty of fluids, bring high-energy snacks. If you get off course or encounter a problem, you’ll be glad you did.
Additionally, depending on where you’re hiking, you may need to dodge rash-inducing plants, including stinging nettles, poison oak, or poison ivy. Bring insect repellent to fend off biting insects and follow prevention strategies for ticks, which may harbor bacteria responsible for Lyme disease and other illnesses. Finally, carry a first aid kit with bandages for cuts and scrapes and moleskin for blisters.
About the Author

Julie Corliss, Executive Editor, Harvard Heart Letter
Julie Corliss is the executive editor of the Harvard Heart Letter. Before working at Harvard, she was a medical writer and editor at HealthNews, a consumer newsletter affiliated with The New England Journal of Medicine. She … See Full Bio View all posts by Julie Corliss
About the Reviewer

Howard E. LeWine, MD, Chief Medical Editor, Harvard Health Publishing
Dr. Howard LeWine is a practicing internist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, Chief Medical Editor at Harvard Health Publishing, and editor in chief of Harvard Men’s Health Watch. See Full Bio View all posts by Howard E. LeWine, MD



















 Each year, more than 4.5 million dog bites occur in the United States. Despite what you might assume, most of these incidents don’t happen when an unfamiliar dog attacks someone in a park or another outdoor location. Instead, most dog bites are inflicted by a pet dog in a home.
Each year, more than 4.5 million dog bites occur in the United States. Despite what you might assume, most of these incidents don’t happen when an unfamiliar dog attacks someone in a park or another outdoor location. Instead, most dog bites are inflicted by a pet dog in a home.











